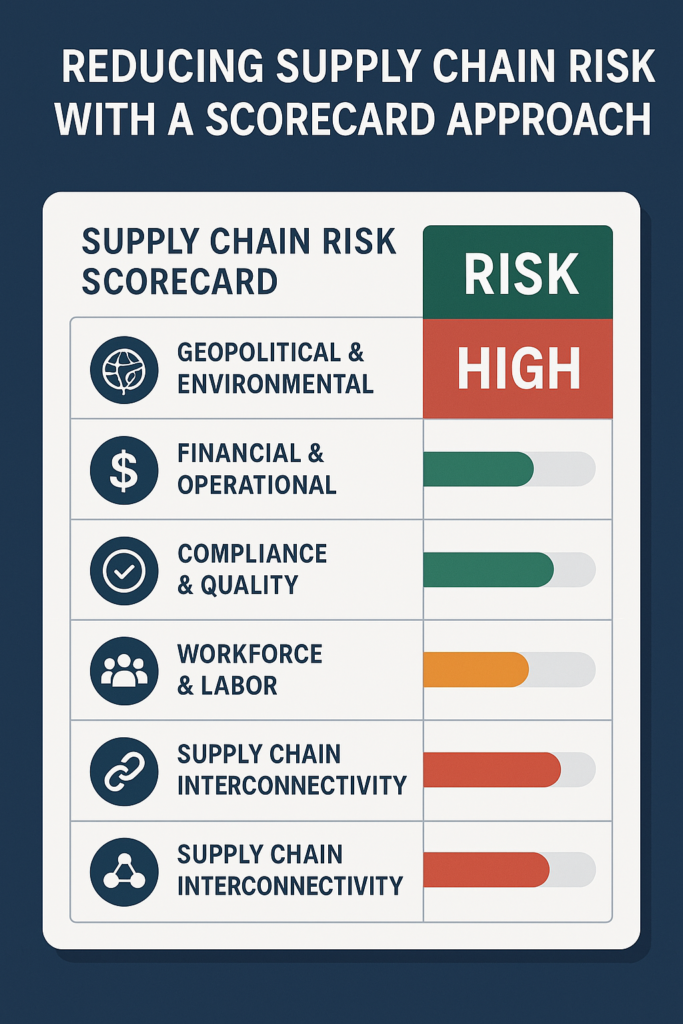
Global supply chains can be disrupted in many ways, including geopolitical instability, environmental disasters, regulatory non-compliance, and financial instability. To mitigate these risks, companies must proactively assess the vulnerability of their suppliers and manufacturing plants. One of the most effective tools for this is a supply chain risk scorecard that systematically evaluates key risk factors across all global manufacturing sites.
Table of Contents
Identifying High-Risk Plants is Critical

A disruption at a facility can lead to product shortages, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage. Identifying which plants pose the greatest risks enables organizations to implement mitigation strategies such as supplier diversification, risk-based inventory management, and compliance auditing.
Key Components of a Supply Chain Risk Scorecard
A well-structured supply chain risk scorecard provides a reliable and quantifiable assessment of potential risks across all supplier plants. Below are the core components of an effective scorecard:
1. Geopolitical & Environmental Risks
- Country Stability Index – Political stability, economic conditions, and trade policies.
- Natural Disaster Vulnerability – Floods, earthquakes, hurricanes, and other environmental risks.
- Regulatory Climate – Trade restrictions, tariffs, and industry regulations.
2. Financial & Operational Risks
- Financial Health of the Supplier – Profitability, debt levels, and financial resilience.
- Production Capacity & Scalability – Ability to meet demand fluctuations.
- Logistical Dependability – Proximity to major markets, transportation reliability, and distribution infrastructure quality.
3. Compliance & Quality Control
- Regulatory Compliance History – FDA, ISO, and other applicable regulatory standards.
- Quality Performance Metrics – Product defect rates, corrective actions, and recall history.
- Cybersecurity & Data Protection – Protection of intellectual property and sensitive business data.
4. Workforce & Labor Stability
- Unionization & Labor Relations – History of strikes or labor disputes.
- Workforce Turnover Rate – High attrition rates may indicate instability.
- Health & Safety Compliance – Workplace safety violations or non-compliance issues.
5. Supply Chain Interconnectivity Risks
- Single vs. Multi-Sourced Components – Dependency on a single supplier increases risk.
- Lead Time Reliability – Consistency in meeting delivery timelines.
- Raw Material Sourcing Risks – Dependency on critical materials with supply constraints.
A Risk-Based Scorecard Approach
Step 1: Data Collection & Weighting
Gather data on each supplier plant across all categories and assign weights based on business priorities. For example, compliance risks have a higher weight for a regulated manufacturer than for a consumer goods company or retailer.
Step 2: Scoring & Risk Categorization
Use a scoring system (1-5 or 1-10 scale) to rank each plant. Aggregate scores can then be used to categorize plants into low, moderate, and high-risk tiers.
Step 3: Actionable Risk Mitigation Strategies
- High-Risk Plants – Establish contingency plans, increase supplier redundancy, conduct frequent audits, and monitor regulatory changes.
- Moderate-Risk Plants – Implement process improvements, negotiate flexible contracts.
- Low-Risk Plants – Maintain ongoing monitoring but allocate fewer resources for immediate intervention.
Conclusion: A Proactive Approach to Supply Chain Resilience
Reducing supply chain risk starts with visibility and assessment. A comprehensive risk scorecard enables businesses to identify weak links in their supply chain and take proactive action before disruptions occur. By incorporating geopolitical, financial, compliance, workforce, and interconnectivity risks into a structured assessment, companies can build a resilient and adaptable supply chain that supports long-term growth and business success.
How do you do it?
How does your company assess supplier risk? Have you implemented a structured approach to evaluating manufacturing plants?
To learn more about Compliance Architects and Supply Chain Risk, fill out the form below to contact us.