In session 3 of the Executive GxP Training, Teresa Gorecki and Jamie Colgin discuss how GMP compliance applies to companies that have outsourced all manufacturing operations. The training also discusses drug, biologics, and combination product GMP requirements for “virtual” companies.
Company sponsors must comply with regulatory standards when outsourcing manufacturing for clinical materials, APIs, drug products, and delivery systems. They are responsible for owning product specifications, managing changes, and overseeing the release of third-party-produced items. Maintaining GMP compliance throughout the product lifecycle is crucial. This encompasses drug, medical device, and combination product requirements for autoinjectors, pre-filled syringes, and specialized nebulizers.
Table of Contents
Regulatory Oversight and GMP Compliance Expectations
FDA and other global regulatory authorities enforce that sponsors maintain responsibility for their products’ quality, identity, purity, safety, and efficacy. This ranges from early-stage clinical development (Phase I) through commercialization. During Phase I, the FDA provides more flexibility under its GMP Guideline for Clinical Trial Material, with strict GMP compliance expected during later stages (Phases II and III).
The requirements are described in Good Manufacturing Practices, ICH Standards, and FDA Guidelines, explaining the importance of a robust Quality System at both the sponsor and contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO/CMO). Effective oversight of outsourced activities is essential.
Industry changes have vastly altered regulations and requirements over the past 25 to 30 years. Outsourcing is typically used to expand capacity, reduce costs, and access specialized capabilities or expertise, with virtual companies using outsourcing as a strategic advantage.
Inspection and enforcement activities have provided valuable lessons for coordinating requirements across global health authorities, including the FDA.
Quality Assurance and Management in Virtual Companies
In virtual companies, Quality Control tasks are mostly outsourced, which requires strong Quality Assurance (QA) and Management practices to ensure compliance and proper quality standards.
Quality Assurance
- Specifications and SOPs: Establish specifications and SOPs for in-house processes within the Sponsor/NDA/BLA Holder.
- Third-Party Providers: Qualify and audit third-party providers regularly.
- Document Review: Approve standards, SOPs, master batch records, and test methods.
- Product Release: Review and approve product releases from third-party providers.
- Change Management: Manage changes impacting production or testing.
- Complaints Investigation: Investigate clinical product quality complaints promptly.
Quality Management
- Oversight: Monitor outsourced activities closely.
- Metrics Review: Assess contractor quality metrics and KQIs.
- Risk Management: Implement a robust Quality Risk Management process.
- Issue Escalation: Quickly escalate critical issues affecting product quality or compliance.
These practices reinforce continuous compliance with regulatory standards and uphold product quality throughout the lifecycle in virtual company settings.
Establishing Essential Processes and Procedures
Effective management of pharmaceutical manufacturing requires structured processes and procedures in several critical areas:
Quality by Design/Design Control
Establishing standards throughout the manufacturing process enforces consistent product quality. This approach supports the transfer of product knowledge and process understanding from development to commercial manufacturing, facilitating post-development changes and optimizations.
Quality Risk Management
It leads the establishment of manufacturing specifications and process structure to assess and mitigate risks associated with changes. It also directs the investigation of issues during manufacturing and testing and informs the development of corrective and preventive actions.
Data Integrity
Enforces the validity and integrity of all data generated during production, testing, and product shipment to ensure reliability throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action)
Focuses on thorough investigation, understanding, and correcting issues while proactively preventing recurrences from maintaining high product quality and compliance standards.
Change Control
Ensures productive management of alterations that could impact product quality or safety. This includes controlling revisions to specifications, process parameters, and procedures to maintain consistent manufacturing standards.
Oversight of Outsourced Responsibilities
Reinforces strict abidance to procedures and specifications by contracted firms involved in manufacturing, maintaining accountability and quality throughout the supply chain.
Quality Systems
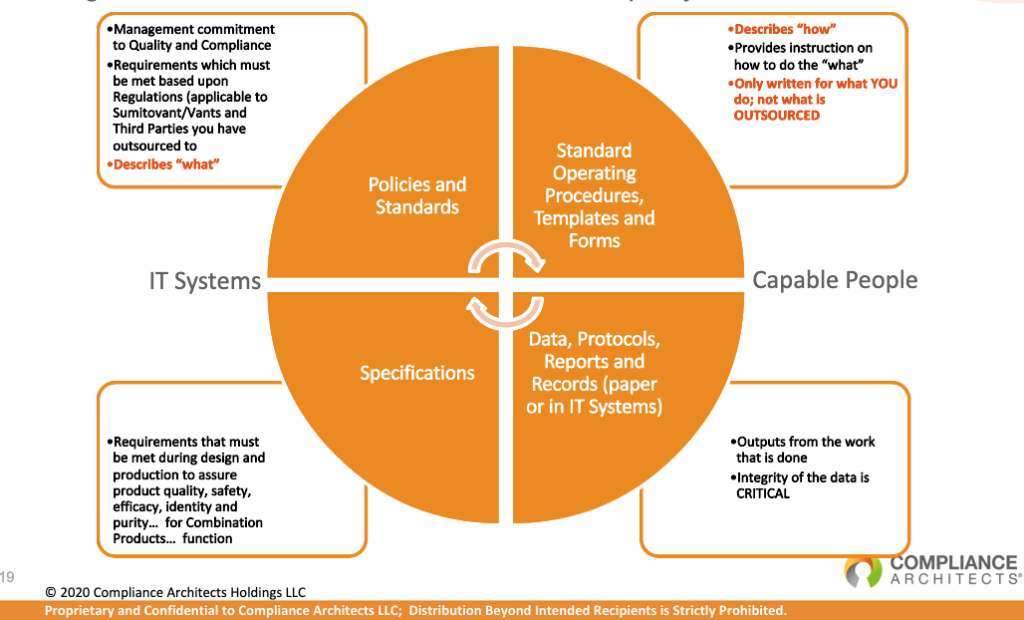
By following quality systems designed by the model above, companies can create environments that create safe and effective operating procedures. This will ultimately result in higher-quality products for patients.
Regulatory GMP compliance and quality assurance play an essential role in pharmaceutical outsourcing. Sponsors must ensure GMP compliance throughout product development, from clinical trials to commercialization. Effective oversight and strong Quality Assurance practices are vital when outsourcing tasks like manufacturing and testing.
Key processes like Quality by Design and Quality Risk Management are critical in maintaining product quality and regulatory adherence. Overall, companies must maintain structured processes and vigilant oversight to uphold standards in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Stay tuned to the final part 4 of this series, where we will focus on Regulatory Compliance Risks.
Fill out the form below to learn more about GMP compliance in companies that outsource manufacturing operations.





